Search results
Author(s):
Eduardo Back Sternick
,
Mariana Faustino
,
Frederico Soares Correa
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Radiofrequency (RF) catheter ablation is currently the treatment of choice in patients with accessory pathways (APs) and Wolff– Parkinson–White syndrome, and is shown to have a success rate >95 %.1 APs usually have endocardial ventricular and atrial insertions, located close to the atrioventricular valve rings, making most endocardial catheter ablation procedures relatively straightforward and…
View more
Author(s):
Rajdip Dulai
,
Fatima Bangash
,
Ajay Sharma
,
et al
Added:
4 months ago
Author(s):
Eleftherios Giazitzoglou
Added:
3 years ago
Dear Sir,
I read with great interest the comprehensive review of Dr Brugada and Dr Keegan on asymptomatic pre-excitation, and the issues of risk stratification and need for catheter ablation.1 Perhaps the authors would like to comment on two additional studies that have just appeared, but contain vital information for the appropriate management of these patients. The first study emanates from a…
View more
Author(s):
Mathieu Lebloa
,
Patrizio Pascale
Added:
1 year ago
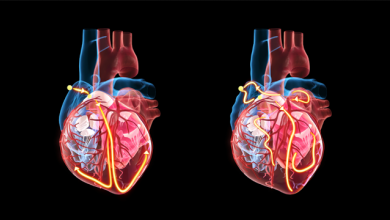
Mahaim Accessory Pathways
Author(s):
Demosthenes G Katritsis
,
Hein J Wellens
,
Mark E Josephson
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Demosthenes G Katritsis
,
Josep Brugada
Added:
3 years ago
The term narrow QRS tachycardia indicates individuals with a QRS duration ≤120 ms, while wide QRS tachycardia refers to tachycardia with a QRS duration >120 ms.1 Narrow QRS complexes are due to rapid activation of the ventricles via the His–Purkinje system, suggesting that the origin of the arrhythmia is above or within the His bundle. However, early activation of the His bundle can also occur…
View more
Author(s):
Demosthenes G Katritsis
,
Mark E Josephson
Added:
3 years ago
Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) denotes re-entry in the area of the AV node, and represents the most common regular arrhythmia in the human.1 Although several models have been proposed to explain the mechanism of the arrhythmia in the context of the complex anatomy and the anisotropic properties of the atrioventricular (AV) node and its atrial extensions (see Figure 1),2 the…
View more
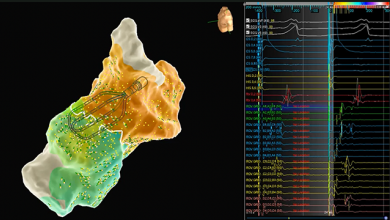
Body Surface Electrocardiographic Mapping for Non-invasive Identification of Arrhythmic Sources
Author(s):
Ashok J Shah
,
Meleze Hocini
,
Patrizio Pascale
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Josep Brugada
,
Roberto Keegan
Added:
3 years ago
The best clinical approach to managing asymptomatic patients with ventricular pre-excitation has yet to be established. The clinical benefit of identifying and treating asymptomatic patients at risk of sudden cardiac death (SCD) has been debated since catheter ablation became effective and safe for the treatment of accessory pathways (APs). Data supporting current recommendations are mostly…
View more
Author(s):
Carina Blomström-Lundqvist
,
Tatjana S Potpara
,
Helena Malmborg
Added:
3 years ago
With the advent of successful surgical repairs and modern diagnostic techniques, an increasing number of patients with congenital heart disease survive to adulthood. Despite these improvements, the surgical corrective atrial incisions performed during childhood lead to subsequent myocardial scarring that have the inherent risk of harbouring substrates for macro-reentrant atrial tachycardias …
View more