Search results
Defining LBBB Patterns in CRT
Author(s):
Roderick Tung
,
Gaurav A Upadhyay
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Demosthenes G Katritsis
Added:
3 years ago
Since its first description by Hays in England in 1906, second-degree atrioventricular (AV) block has been a fascinating clinical entity, mainly due to obscure points regarding its diagnosis that emanate from misconceptions and errors regarding its proper definition.1–3 The practicing clinician should be aware of the following points that may assist a proper diagnosis and, consequently, accurate…
View more
Author(s):
Steven M Markowitz
,
George Thomas
,
Christopher F Liu
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Pioneering electrophysiology studies in the 1990s defined the anatomical boundaries of typical atrial flutter, identified regions for effective catheter ablation of this arrhythmia and described procedural endpoints to minimise recurrences after ablation. Activation and entrainment mapping demonstrated that typical flutter arises from reentry around the tricuspid annulus.1 Criteria to confirm…
View more
Anisotropic Cardiac Conduction
Author(s):
Irum D Kotadia
,
John Whitaker
,
Caroline H Roney
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Francisco G Cosio
Added:
3 years ago
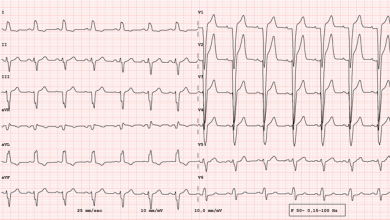
The term ‘flutter’ was coined to designate the visual and tactile rapid, regular atrial contraction induced by faradic stimulation in animal hearts, in contrast with irregular, vermiform contraction in atrial fibrillation (AF).1,2 On the ECG, flutter was a regular continuous undulation between QRS complexes at a cycle length (CL) of ≤250 ms (≥240 bpm). Slower tachycardias displaying discrete P…
View more
Author(s):
Stephen P Page
,
Mehul Dhinoja
Added:
3 years ago
Over the last 30 years, the role of catheter ablation for treating a wide range of arrhythmias has increased dramatically. The electrophysiological substrates of the more straightforward arrhythmias (such as atrio-ventricular reciprocating tachycardia and atrio-ventricular nodal re-entry tachycardia) have now been well defined and excellent long-term success rates can be achieved at minimal risk…
View more
Author(s):
Frits Prinzen
,
Joost Lumens
,
Jürgen Duchenne
,
et al
Added:
2 years ago
Author(s):
Caroline H Roney
,
Andrew L Wit
,
Nicholas S Peters
Added:
3 years ago
Determining optimal treatment strategies for complex arrhythmogenesis in AF is confounded by the lack of consensus on the mechanisms causing AF. Fundamental to defining arrhythmogenic mechanisms of AF are the distinctions and interplay between functional features (determined by the electrophysiology of a cell) and structural features (determined by whether a structural or anatomical feature is…
View more
Author(s):
Fatima M Ezzeddine
,
Isaac G Leon
,
Yong-Mei Cha
Added:
8 months ago
Author(s):
Jean-Baptiste Gourraud
,
Jason G Andrade
,
Laurent Macle
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia observed in clinical practice, occurring in approximately 2 % of the general population.1–3 A progressive increase in both the prevalence and incidence of AF has been demonstrated in recent years, defining AF as a major economic and public health issue.1
The identification of sites of AF initiation and/or maintenance within…
View more