Search results
AF Ablation in HFpEF
Author(s):
Nicolas Johner
,
Mehdi Namdar
,
Dipen Shah
Added:
1 year ago
Article
Author(s):
Marius Andronache
,
Nikola Drca
,
Graziana Viola
Added:
3 years ago
AF is the most common sustained cardiac arrhythmia in clinical practice. It is associated with increased risk of stroke and heart failure (HF), and is a significant global health challenge.1 Catheter ablation procedures, which isolate the pulmonary veins (PV) from the left atrium and prevent AF initiation, are effective and safe treatment options, and have emerged as the preferred rhythm control…
View more
LBBAP in Heart Failure
Author(s):
Juan Carlos Diaz
,
Mauricio Duque
,
Julian Aristizabal
,
et al
Added:
4 months ago
Article
Author(s):
Laurent Roten
,
Matthew Daly
,
Patrizio Pascale
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
With an ageing population and widespread use of implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, physicians are confronted with an increasing number of patients with symptomatic, drug-refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT). Catheter ablation is an important treatment option in the management of patients with structural heart disease and VT.1,2 In many patients, VT can be successfully ablated from the…
View more
Author(s):
George D Katritsis
,
Vishal Luther
,
Prapa Kanagaratnam
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
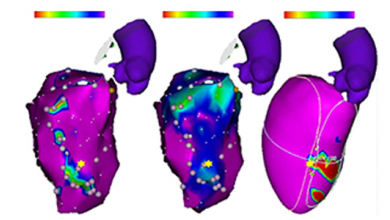
The introduction of cardiac electroanatomic mapping systems in the mid-1990s has permitted investigators to record intracardiac electrograms (EGMs) with accurate spatial localisation in 3D.1 These 3D mapping systems have enabled the display of the cardiac chambers as an anatomical shell upon which voltage, or activation, information can be displayed. Most commonly, colour is used to represent the…
View more
Author(s):
Yunqiu Jiang
,
Sunny S Po
,
Faris Amil
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Imbalance of the autonomic nervous system (sympathetic/parasympathetic) is known to contribute to the pathophysiology of multiple cardiovascular diseases, including AF, MI (and related ventricular arrhythmias) and heart failure. The concept of neuro-immune axis has been proposed to tightly integrate the brain–heart–periphery axis, which is characterised by various pathways of the anti…
View more
Author(s):
Ling Kuo
,
Jackson J Liang
,
Saman Nazarian
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Catheter ablation has been increasingly used as a treatment for refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients with non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy (NICM). However, ablation outcomes tend to be quite variable because of the heterogeneity of the aetiology for the NICM and associated VT substrate in these patients.1–3 Patients with NICM can be sub-classified based on specific genotypic and…
View more
Author(s):
Sebastiaan RD Piers
,
Katja Zeppenfeld
Added:
3 years ago
Over the last 20 years ventricular tachycardia (VT) ablation has evolved from a treatment modality for selected patients withrecurrent haemodynamically tolerated VT (which can be mapped during ongoing arrhythmia), to a therapeutic option for patients with tolerated and untolerated VT using substrate-based ablation strategies.1 The substrate for VT after myocardial infarction (MI) consists of…
View more
Author(s):
Baldeep S Sidhu
,
Justin Gould
,
Mark Elliott
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Author(s):
Mouhannad M Sadek
,
Robert D Schaller
,
Gregory E Supple
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Scar-related reentrant ventricular tachycardia (VT) may be present in a variety of structural heart disease (SHD) phenotypes. In this setting, VT circuits are comprised of viable myocytes separated by fibrosis, allowing for the slow conduction needed to facilitate reentry.1,2 Aetiologies of fibrosis include ischaemic heart disease (IHD), inflammatory conditions, infiltrative cardiomyopathy,…
View more











 « First
« First