Search results
Author(s):
Sebastiaan RD Piers
,
Katja Zeppenfeld
Added:
3 years ago
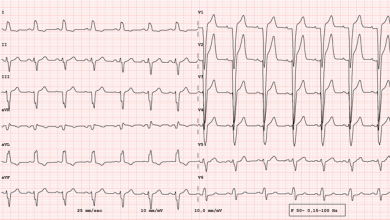
Over the last 20 years ventricular tachycardia (VT) ablation has evolved from a treatment modality for selected patients withrecurrent haemodynamically tolerated VT (which can be mapped during ongoing arrhythmia), to a therapeutic option for patients with tolerated and untolerated VT using substrate-based ablation strategies.1 The substrate for VT after myocardial infarction (MI) consists of…
View more
Author(s):
Cristian Podoleanu
,
Jean-Claude Deharo
Added:
3 years ago
The increasing use of cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) for management of cardiac conditions has over the last few years been associated with higher infection rates.1 Expanded CIED use alone cannot account for this rise,2–4 which involves both patient- and device-related factors. Indeed patients are tending to be older and presenting with co-morbidities, while devices are becoming…
View more
Author(s):
Nisha Gilotra
,
David Okada
,
Apurva Sharma
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
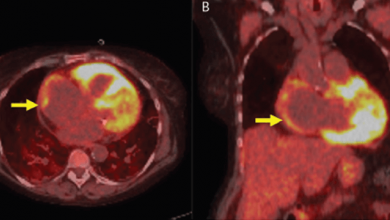
Sarcoidosis is an inflammatory granulomatous disease that can affect any organ. Systemic sarcoidosis is known to affect young adults, with a second peak in women >50 years of age, as demonstrated in Scandinavian and Japanese studies.1–4 In the US, the lifetime risk of sarcoidosis is 2.4% for black people and 0.85% for white people.1 The incidence of cardiac involvement has been increasingly…
View more
Author(s):
Ling Kuo
,
Jackson J Liang
,
Saman Nazarian
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
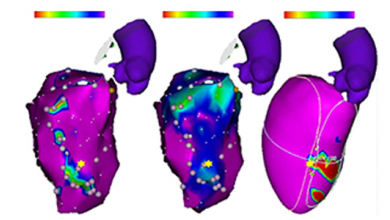
Catheter ablation has been increasingly used as a treatment for refractory ventricular tachycardia (VT) in patients with non-ischaemic cardiomyopathy (NICM). However, ablation outcomes tend to be quite variable because of the heterogeneity of the aetiology for the NICM and associated VT substrate in these patients.1–3 Patients with NICM can be sub-classified based on specific genotypic and…
View more
Author(s):
Brenton S Bauer
,
Anthony C Li
,
Jason S Bradfield
Added:
3 years ago
Ventricular arrhythmias (VA) are commonly associated with structural heart disease and have substantial impact on patient outcomes and health system costs. Within the realm of cardiomyopathy (CM), there has been substantial progress with respect to ischaemic CM (ICM) in the understanding of infarct related scar biology and scar-mediated ventricular tachycardia (VT).
This has led to interventions…
View more
Author(s):
Rikke Esberg Kirkfeldt
,
Jens Brock Johansen
,
Jens Cosedis Nielsen
Added:
3 years ago
Cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED) therapy is effective and safe. However, infections related to CIED treatment may have devastating consequences, causing significant morbidity, mortality and generating considerable healthcare costs.1–6 Temporal trends in CIED treatment indicate a disproportional increase in CIED infections relative to implantation rates.1,7,8 Reasons for this trend are…
View more
Author(s):
Frits Prinzen
,
Joost Lumens
,
Jürgen Duchenne
,
et al
Added:
2 years ago
Author(s):
Adryan A Perez
,
Frank W Woo
,
Darren C Tsang
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
The use of cardiovascular implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) has increased dramatically, with approximately 1.2–1.4 million CIEDs implanted annually worldwide.1 In the US alone, there are more patients with CIEDs than registered nurses.2,3 CIEDs use leads that connect a generator to cardiac tissue to treat patients with many conditions including symptomatic bradycardia, morbid tachycardia…
View more
Body Surface Electrocardiographic Mapping for Non-invasive Identification of Arrhythmic Sources
Author(s):
Ashok J Shah
,
Meleze Hocini
,
Patrizio Pascale
,
et al
Added:
3 years ago
Article
Author(s):
Haipeng Tang
,
Shaojie Tang
,
Weihua Zhou
Added:
3 years ago
Cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT) is a widely-performed standard treatment for improving cardiac function and quality of life in patients with heart failure.1 After CRT, however, 30–40 % of patients do not experience improvements in left ventricular (LV) function and clinical symptoms.2–3 The key factors for increasing the response rate to CRT are identification of the optimal LV lead…
View more